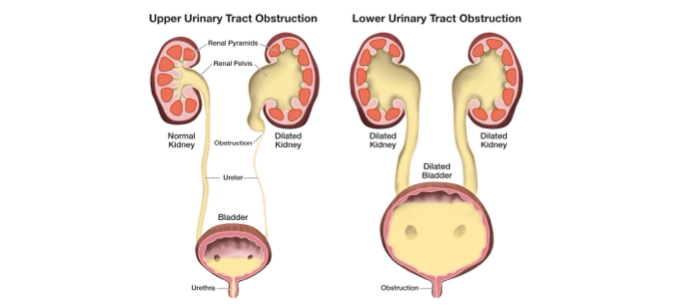
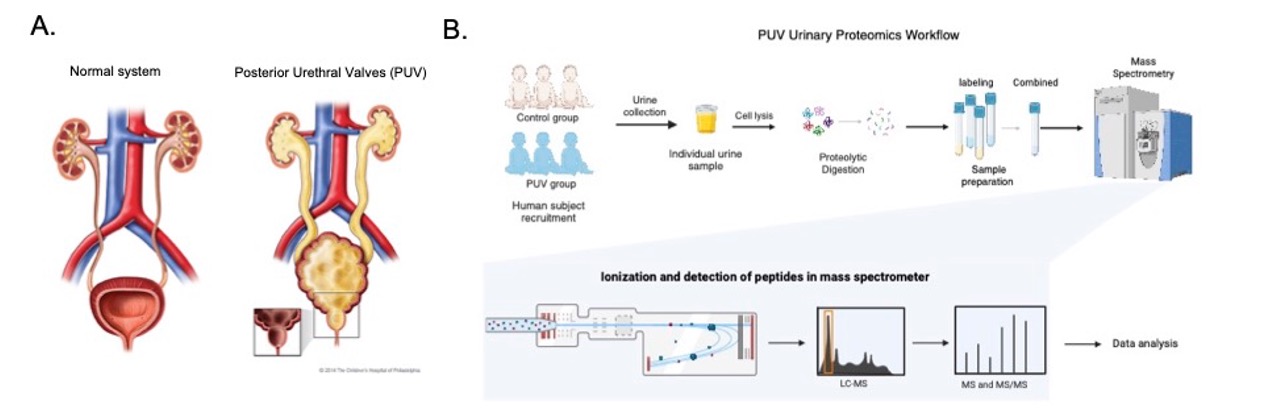
Urinary Tract Obstruction
a project of UTO influence on kidney, ureter and bladder
Urinary tract obstruction refers to any condition that disrupts the natural flow of urine through the urinary system, encompassing the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. This blockage can arise from various sources such as kidney stones, tumors, congenital anomalies, or prostate enlargement in males. When the urinary tract is obstructed, urine accumulates in the kidneys, causing increased pressure that can lead to intense pain, urinary tract infections, and potentially irreversible kidney damage if not addressed promptly. Symptoms may manifest as difficulty urinating, frequent urination, flank pain, hematuria, and abdominal swelling. Timely diagnosis and intervention are essential to alleviate symptoms, avert complications, and restore proper urinary function. Treatment approaches vary based on the underlying cause of obstruction and may involve medications, minimally invasive procedures, or surgical interventions.
You can also access to the project details in my github: